Pharmacokinetics
GHRP-6 has a well documented and understood mechanism of action. GHRP-6 is a synthetic peptide, and is an analog to met-enkaphalin. Met-enkaphalin is a compound that acts primarily on receptors in the gut, called ghrelin receptors. These receptors regulate hunger levels, as well as the release of human growth hormone.[2] When introduced, GHRP-2 increases the production of growth hormones by interacting with ghrelin receptors.[1]
Scientific Studies
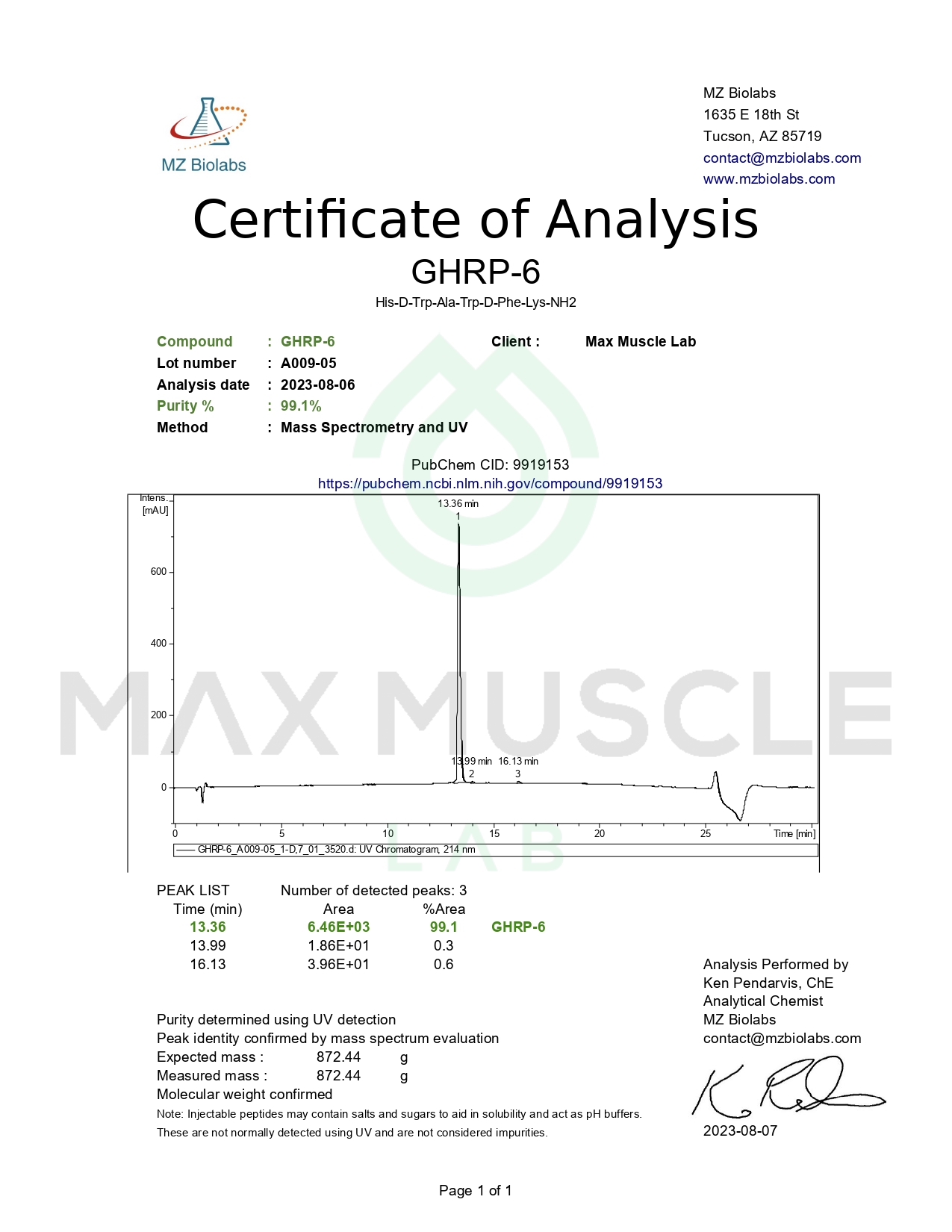
Studies have revealed potential links between GHRP-6 and higher levels of growth hormones. In a study on individuals with hypothyroidism, GHRP-6 was acutely administered intravenously. Levels of growth hormone were then monitored. Results appeared to indicate a correlation between GHRP-6 and greater levels of human growth hormone.[3] Another study on rats seems to corroborate with the prior findings. Following administration, growth hormone levels appeared greater.[4]
Sources:
[1] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928098712003880?via%3Dihub
[2] http://www.eurekaselect.com/118430/article
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9156038
[4] https://academic.oup.com/endo/article/151/5/2008/2456511
[5] https://annals.org/aim/article-abstract/732002/systematic-review-safety-efficacy-growth-hormone-healthy-elderly?doi=10.7326%2f0003-4819-146-2-200701160-00005
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5392015/
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2824650/
[8] https://www.verywellhealth.com/injection-side-effects-call-doctor-2616542