Pharmacokinetics
IGF-1 LR3 is a synthetic version of the IGF-1 hormone. As an analog of this hormone, its mechanism of action is much the same.[1] IGF-1 is one of the many proteins released as a result of human growth hormone, or hGH, interaction. As hGH interacts with cells through the body, it eventually comes into contact with the liver cells. After reacting, IGF-1 is released.[2] IGF-1 then begins reacting with almost all cells as it travels through the body, stimulating their growth. However, IGF-1 has a very short half-life, as it is quickly disabled by insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, or IGFBP.[3]
IGF-1 LR3 counteracts this inhibition through its structure. Being elongated, IGF-1 LR3 circulates throughout the body much longer than IGF-1. This is due to its structure being incompatible with IGFBP, and therefore it avoids being binded.[1]
Scientific Studies
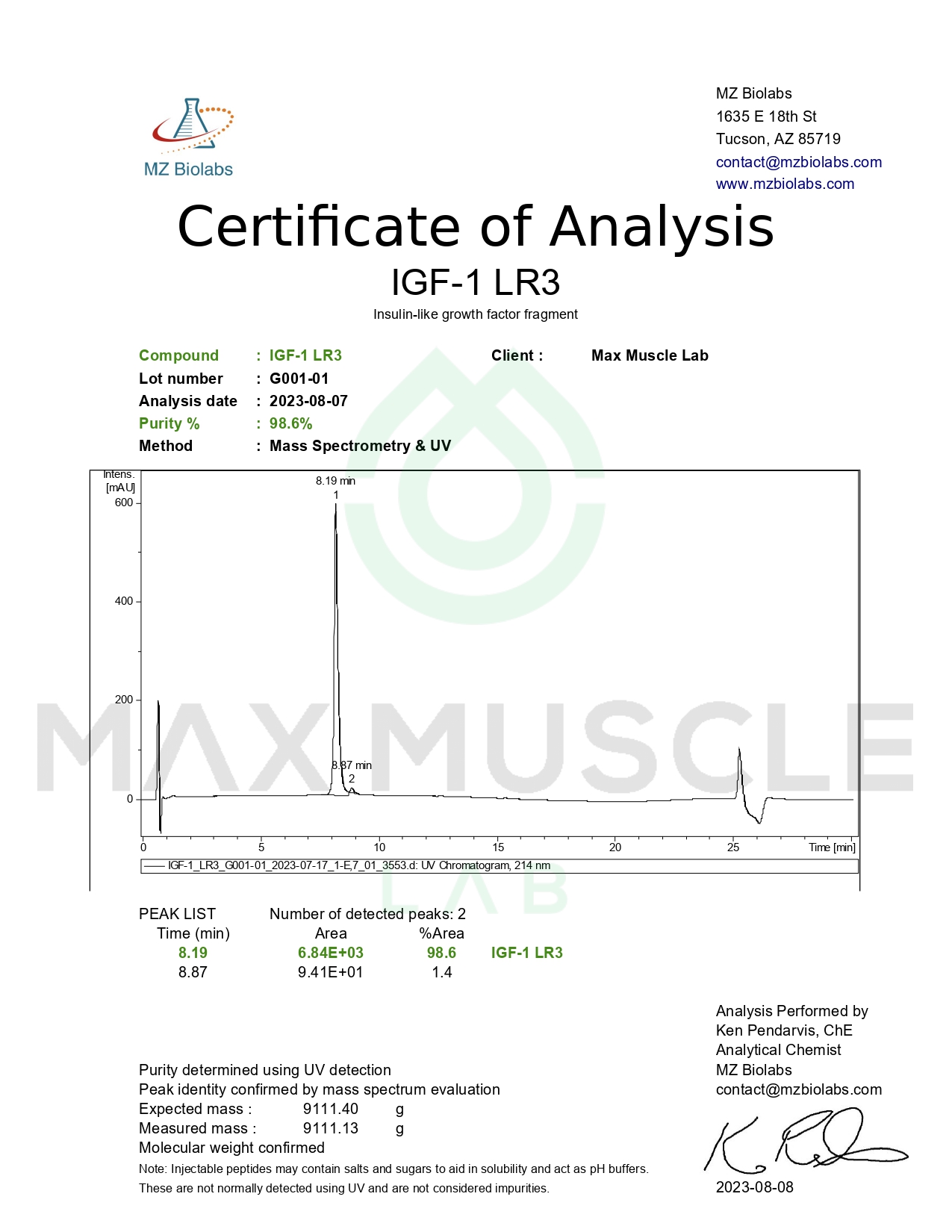
A study into IGF-1 LR3 shows some anabolic action. IGF-1 LR3, among other IGF-1 analogs, was injected subcutaneously into several rats daily for a week. At the end of the study, the effects of the analog were noted as positive. IGF-1 LR3 prevented catabolic responses in the subjects, and appeared to influence muscle and organ weights and efficiencies.[1]
Sources:
[1] https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/150/1/joe_150_1_010.xml?pmid=8708565&view=long
[2] https://www.jci.org/articles/view/15463
[3] https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/175/1/19.xml?pmid=12379487&view=long
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3069834/
[5] https://www.verywellhealth.com/injection-side-effects-call-doctor-2616542